RNA Storage buffer is 1 mM sodium citrate pH 6.4 in RNase-free water. The buffer is recommended for precipitate dissolving and long-term storage of RNA after e.g. RNA isolation using organic solvents like RNA Extracol (cat. no. E3700). RNA is stabilized in the solution by low pH (6.4) preventing from the nucleic acids hydrolysis and by ions chealation by citrate, which in turn inhibit RNase and DNase activity. RNA dissolved in RNA Storage can be used directly for reverse transcription, RT-qPCR, etc.
RNA Storage buffer is recommended for precipitate dissolving and long-term storage of RNA. RNA is stabilized in the solution by low pH (6.4) preventing from the nucleic acids hydrolysis and by ions chealation by citrate, which in turn inhibit RNase and DNase activity. RNA dissolved in RNA Storage and kept in -80°C is more stable than RNA stored in DEPC water (RNase-free).
 |
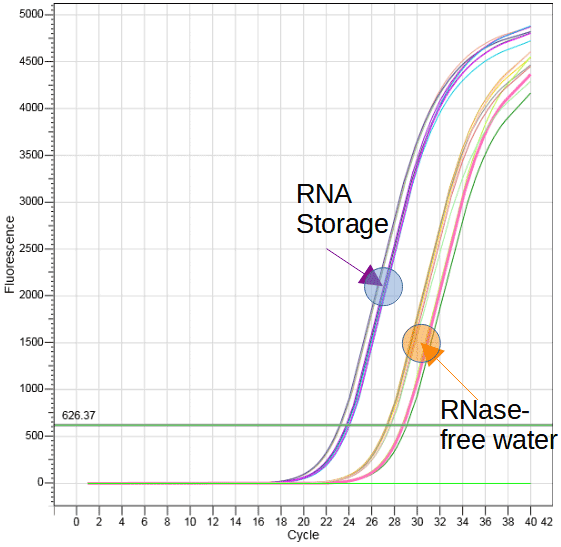 |
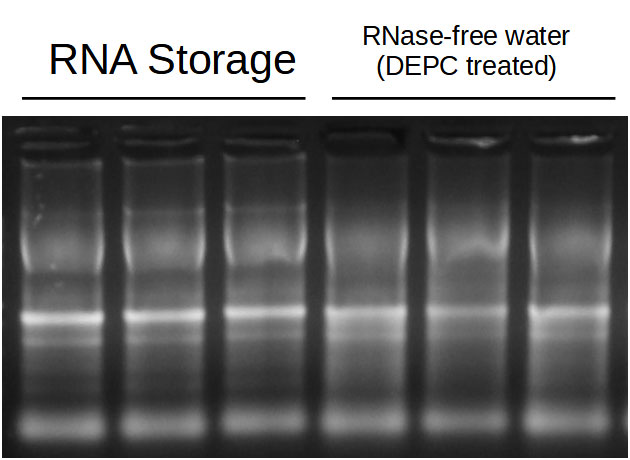
| Fig. 1. Gel electrophoresis of RNA stored in +4 °C for 2 months. | Fig. 2. RT-qPCR on the template of RNA stored in +4 °C for 2 months. |
To compare the RNA stability in RNA Storage buffer and in DEPC water, the samples were incubated in unfavourable conditions for RNA, afterwards the gene expression level was established.
RNA from the liver of Sus scrofa was purified with RNA Extracol (cat. no E3700) and dissolved in RNA Storage (cat. no E0308) or RNase-free water (DEPC treated) (cat. no E0210). The obtained samples were incubated in +4 °C for 2 months (Fig. 1). The storage temperature of +4 °C was chosen in order to accelerate the RNA degradation process. cDNA was obtained with the use of smART First Strand cDNA Synthesis kit (cat. no E0804) and oligo(dT)20 primers. qPCR reaction with Fast SG qPCR Master Mix (2x) (cat. no E0411) and transcript specific primers was made. Fig. 2 shows SYBR Green fluorescence of samples dissolved in RNA Storage buffer and RNase-free water. The difference in gene expression level points to the conclusion that RNA molecules in RNA Storage buffer are indeed more resistent to degradation.

